01. Greenhouse
Styles
02.
Greenhouse Structures
03. Greenhouse
Coverings
04. Greenhouse
Site Selection
05. Site
Preparation and Foundation
06. Ventilation
& Cooling
07. Air
Circulation
08. Shading
09. Heating
10. Thermometers
Greenhouses come in many different design configurations. The most important decision is to determine whether a freestanding or home-attached model best suits your needs. The freestanding variety allows you to select the appropriate site to maximize sunlight exposure, maximum versatility and aesthetic appeal for your landscape. The home-attached variety offers convenient access to services, easily accessible, efficient use of yard space and added insulation. Another point of consideration is choosing your aesthetic design. The different roof slopes options and curved eave or straight eave often depend on personal taste and architectural style.
 Click on image to enlarge
Click on image to enlarge
When selecting your frame type thought should be given to longevity, strength, versatility and maintenance requirements. Additionally, consideration should be given to the weather tightness of the greenhouse with respect to drafts and water penetration.
Attain the best balance between insulating values, aesthetics and economy to suit your needs. There are many different glazing options on the market today. Glass gives a timeless look and with full light transmission allows greenhouse gardeners to have the capability to control all growing variables. Alternatively, different types of plastics are available which provide more selections when determining what suits your budget and fundamental requirements. For more information visit Glazing Systems.
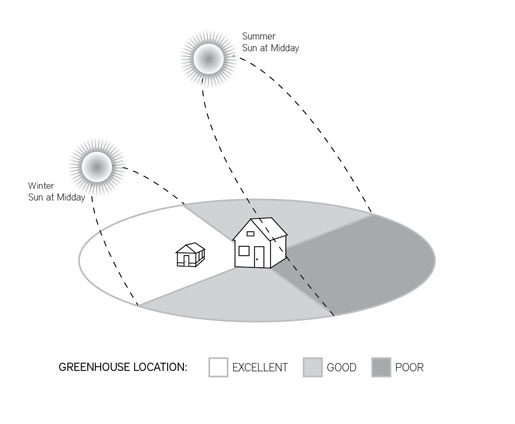
When selecting a site for your foundation, choose a flat, level surface where your greenhouse can be easily installed, stable and secure. Locate your greenhouse close to power and water, while also considering water drainage and easy access. Try to locate the greenhouse so that 6 hours of sunlight is available during winter months.
The most common foundations for hobby greenhouses are wood frame or concrete. Wood frames are selected for their ease of preparation and allow for long term flexibility in case the greenhouse is ever to be moved or extended. Concrete can be chosen for a more permanent site and will last for generations.
Pressure treated wood now requires a 10 mm polyethylene barrier between wood and aluminum sill to prevent corrosions of aluminum. A hobby greenhouse under (100 sq. ft.) can be fastened to a 4" x 4" or 4" x 6" treated wood timber foundation. For a larger greenhouse a 6" x 6" beam is recommended. Wooden timbers can be stacked to increase the height of the greenhouse.
When choosing a more permanent site, concrete slabs or concrete footings may be installed. Bricks or masonry blocks may also be used, but ensure the top bricks are closed off, so it has a flat surface to fasten the greenhouse to. All foundations must be level and square for easy installation of the greenhouse structure. Check your local building codes regarding site requirements and if a permit is required.
A foundation sketch will be supplied showing all outside dimensions in which to build.
The main goal of greenhouse gardening is to provide a controlled environment for the plants you are growing. In warm months and sunny days, this requires a source for cool air intake. There are two primary forms of cooling your greenhouse.
Passive ventilation is still the most popular form of cooling as it is the most natural and gentle for your plants. This is achieved through automatic ridge vents and optional side venting. Relying on convection, the hot air will naturally rise out and lower cooler air can be drawn through the lower openings.
For larger greenhouses or hotter climates, a forced ventilation system may be necessary to ensure the greenhouse does not over heat. This will usually include a combination of exhaust fan, motorized intake shutters and thermostat, providing a more controlled environment. When choosing a forced ventilation system, plan on relying on it for most of spring, summer, and fall; during the colder winter months a passive ventilation method through venting offers a less extreme temperature fluctuation.
Diffusing the sun`s light will also minimize heat build up and harmful rays. Many plastic coverings act as a built in shade system. With a glass greenhouse, some form of shading will be required if there is not adequate natural shade available.
Air circulation is required any time there are plants in the greenhouse. This constant movement of air helps to keep an even temperature throughout the greenhouse. As well, this reduces condensation which reduces mould, fungus and diseases.
During the spring and summer, direct sunlight can quickly overheat the greenhouse and destroy both plants and seedlings. Exterior shading is the most effective method of preventing heat build-up. Shade cloth, or screening material, has been used by commercial growers for many years and is now available for hobby greenhouses. Higher density shade cloth is more suitable for orchids or other tropicals.
Many gardeners choose a greenhouse because they like to garden year round. The heat requirements for your greenhouse is dictated by the type of plants you are growing, the size of your greenhouse, the greenhouse cover material and your climate zone.
The type of plants will determine whether your greenhouse is a cool, warm or hothouse. A cool house maintains a night temperature of 40 – 45 oF (5 - 7 oC), A warm greenhouse requires a night temperature of 55 oF (13 oC) for plants that require a warmer environment. Hothouses require a nigh temperature of 65 oF (18 oC) for orchids or tropical plants.
Once a greenhouse use has been chosen, heating requirements can be easily worked out and are available by contacting our friendly staff.
Probably the most important accessory in a greenhouse will be your maximum –minimum thermometers. This allows gardeners to record daytime high as well as overnight low temperatures ensuring you can correctly control your growing environment.
